
Recursos Educativos en inglés - Coloring Pages Thanksgiving
Láminas para Colorear en Inglés
Acción de gracias
02. Thanksgiving. Banquete acción de gracias
Para Imprimir la lámina, se recomienda, guardarla primero en el PC.

02. Thanksgiving. Banquete acción de gracias
Para Imprimir la lámina, se recomienda, guardarla primero en el PC.

(Sung To:Are you sleeping?)
We eat turkey, we eat turkey
Oh so good, oh so good
Always on Thanksgiving, always on Thanksgiving
Yum,yum,yum... yum,yum,yum
We eat pumpkin pie, we eat pumpkin pie
Oh so good, oh so good
Always on Thanksgiving, always on Thanksgiving
Yum,yum,yum... yum,yum,yum
We eat yams, we eat yams
Oh so good, oh so good
Always on Thanksgiving, always on Thanksgiving
Yum,yum,yum... yum,yum,yum
We eat mashed potatoes, we eat mashed potatoes
Oh so good, oh so good
Always on Thanksgiving, always on Thanksgiving
Yum,yum,yum... yum,yum,yum
Let your children make up their own verses
(Thanks so much to nany83 for sending in this song!)
Canciones para niños en inglés para Acción de gracias. Ideales para favorecer el aprendizaje del idioma, adquirir vocabulario, practicar la pronunciación, etc.

To y for son de esas palabras difíciles de usar. Son especialmente problemáticas en la escritura, incluso para quienes tienen un buen nivel de inglés.
To y For suelen ser preposiciones, pero no siempre. Por ejemplo, podemos utilizar TO para marcar el infinitivo de un verbo. To play significa jugar, en infinitivo. También los utilizamos a veces para crear verbos compuestos (los famosos phrasal verbs, como look for, plan for, etc.).
She want work to earn money. Ella quiere trabajar para ganar dinero.
This is for you. Esto es para ti
Podemos ver la diferencia aquí: en un caso, hay un verbo (earn). En el otro caso, hay un sustantivo, o grupo de sustantivos (for you).
Cuando queramos expresar la meta, el motivo, el objetivo, el objeto, pondremos:
TO + Verbo o FOR + sustantivo
Podremos ver FOR + verbo en ING, cuando hablemos del uso de un objeto. Por ejemplo, al responder a la pregunta "What is it for ?" It’s a mug, it’s for drinking coffe. ¿Para qué sirve? Es una taza, es para beber café.
Cuando haya una noción de transferencia, o de dirección con movimiento, utilizaremos To.
En su defecto, diremos:
This present is for María. Es un estado, no existe la noción de transferencia.
Regla 2: Noción de transferencia, de movimiento, utilizaremos TO.
Hasta aquí las dos formas principales de elegir entre To y For.

Should y must son modales que se utilizan para expresar la noción de deber u obligación, pero en diferentes grados.
En resumen, must expresa obligación, mientras que should expresa la idea "debería", que es menos fuerte que la obligación.
Si yo digo:
You must work if you want to succeed. Esto significa que debes trabajar, estás obligado a hacerlo, si quieres tener éxito.
Esto es más fuerte que si hubiera dicho "You should work if you want to succeed." En este caso, la idea es más bien que "debes trabajar si quieres tener éxito". Es más bien un consejo, una sugerencia.
Tomemos un segundo ejemplo, con el must, y luego con el should:
You must eat now. Debes comer ahora. Es una obligación, debes hacerlo.
Según el contexto, es una orden, o una situación en la que es muy importante comer inmediatamente.
Por otro lado, si tomo la misma frase con should, se da:
You should eat now. En este caso, estoy diciendo que "deberías comer ahora". Es un consejo que te doy, una recomendación. No es tan fuerte como con con must.
Must en la forma negativa se escribe must not o mustn't. Ambos significan lo mismo.
Expresan exactamente lo contrario del must: es decir, la prohibición.
Pongamos un ejemplo:
You mustn’t walk on the carpet. No debes pisar la alfombra. Lo que significa que debes mantenerte alejado de la alfombra.
Should en la forma negativa se escribe should not o should't. Expresa una crítica o sugerencia más bien negativa. Significa "no debes...".
Tomemos el mismo ejemplo:
You shouldn’t walk on the carpet. No deberías pisar la alfombra. Te estoy dando el consejo, te estoy diciendo que no debes caminar sobre ella. También en este caso, no es tan fuerte como el mustn't.
También podemos utilizar must para traducir algo de lo que estamos bastante seguros. Por ejemplo, digamos que no tengo reloj, pero estoy seguro de que son las diez. Puedo decir: It must be around 10 o’clock now. Deben ser alrededor de las 10 en punto.

Puedes dudar entre el must y el have to. ¡Es cierto que son muy parecidos! En la forma afirmativa, ambos expresan obligación. La diferencia está en la forma negativa. Te lo explico todo a continuación:
Must es un modal, o auxiliar modal. Aquí tienes una lección específica sobre MUST.
Se utiliza justo antes de la base verbal.
I must do my food. Debo hacer mi comida. (obligación).
Vemos que justo después de must, pongo una base verbal, es decir, el infinitivo, sin la palabra To. Esto es invariable. Nunca habrá una conjugación después de MUST o después de cualquier modal.
Talk, study, be: Vemos que sea cual sea el verbo, no hay conjugación después de Must.
Es casi lo mismo, pero (necesariamente), está el TO antes del verbo. Tomemos el mismo ejemplo:
I have to do my food. Tengo que hacer mi comida. (obligación).
Do está en infinitivo y también es invariable.
Talk, study, be: Los verbos están en infinitivo y, por tanto, también son invariables.
Como hemos visto en los ejemplos anteriores, ambas formas expresan la obligación en sentido afirmativo.
Para ser realmente precisos, podemos señalar que hay pequeños matices entre ambos. De hecho, have to se utiliza cuando la obligación viene de fuera, cuando alguien o algo distinto a nosotros nos impone la obligación. Pero es una cuestión de matiz, y se pueden utilizar las dos expresiones indistintamente, porque están muy cerca.
Volvamos al mismo ejemplo, pero con Mustn't (o Must Not, es lo mismo):
Esto significa que NO DEBO hacer la comida.
Sin embargo, si utilizo Don't have to, el significado NO es el mismo:
Esto significa que no tengo que hacer la comida.
Mustn't es la prohibición.
Don't have to no es ninguna obligación.

If you think you're beaten,
you are.
If you think you don't dare,
you won't.
If you think you'd like to win but you can't,
you won't.
If you think you will lose,
you have already lost.
Because in the world you will find
that success begins
in the will of man
It's all in the state of mind.
For many a race has been lost
Before they have been run.
And many a coward has failed
Before they have begun their work.
Think big
and your achievements will be realised.
Think small
and you will be left behind.
If you think you are ahead,
you already are.
You have to be sure of yourself
before you try to win a prize.
Put your mind and your will
in a positive attitude.
The battle of life,
is not always won
the strongest man
or the lightest.
Because sooner or later
the man who wins
is the one who
THINKS HE CAN DO IT
C. Barnard
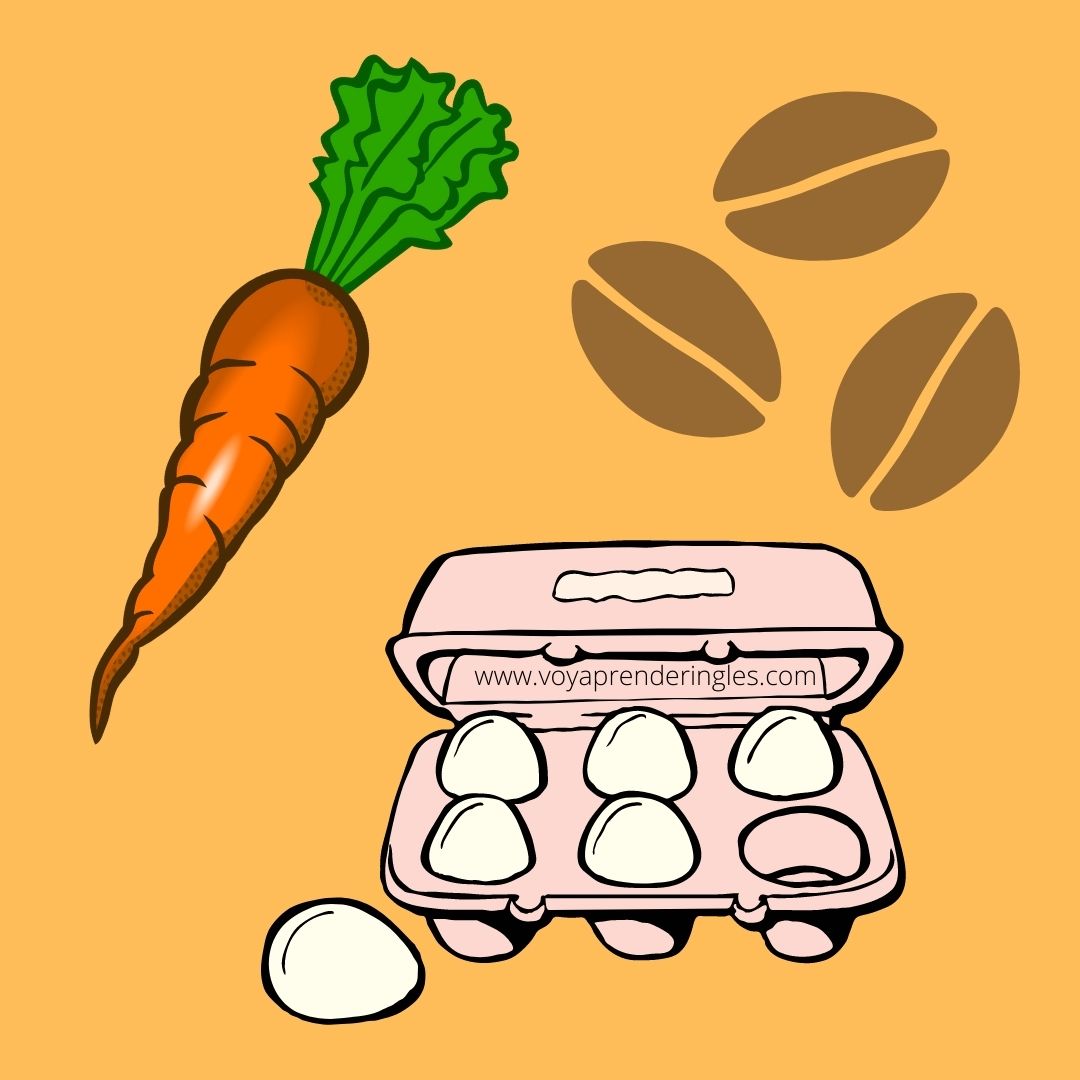
A daughter was complaining to her father about her life and how things were so difficult for her, She didn't know how to go on and thought she would give up, She was tired of struggling, it seemed that when she solved one problem, another would appear.
Her father, a chef, took her to his workplace, where he filled three pots with water and placed them over a high flame, soon the water in all three pots was boiling, in one he put carrots, in another he put eggs and in the last he put coffee beans, he let them boil without saying a word.
The daughter waited impatiently, wondering what her father was doing. After twenty minutes the father turned off the fire, took out the carrots and put them in a bowl, took out the eggs and put them in another bowl, put the coffee beans and put them in a third bowl.
Looking at his daughter he said, "My dear, what do you see?" "Carrots, eggs and coffee" was her reply, he made her come closer and asked her to touch the carrots, she did so and noticed that they were soft, then he asked her to take an egg and break it, after taking off the shell, she observed the hard boiled egg, then he asked her to taste the coffee, she smiled as she enjoyed its rich aroma.
Humbly the daughter asked, "What does this mean, Father?" he explained that the three elements had faced the same adversity: boiling water, but had reacted differently.
The carrot had come to the water strong, hard, but after passing through the boiling water it had become weak, easy to break, The egg had come to the water fragile, its thin shell protected its liquid interior, but after being in boiling water, its interior had hardened, The coffee beans however were unique, after being in boiling water, they had changed to water.
What are you, he asked his daughter, "When adversity knocks at your door, how do you respond, are you a carrot, an egg or a coffee bean? And what are you like, my friend, are you a carrot that looks strong but when adversity and pain touch you, you become weak and lose your strength?
Are you an egg, starting with a malleable heart? You possessed a fluid spirit, but after a death, a separation, a betrayal, a dismissal you have become hard and rigid? On the outside you look the same, but are you bitter and harsh, with a hardened spirit and heart? Or are you like a coffee bean? Coffee changes to boiling water, the element that causes you pain.
When the water reaches boiling point the coffee reaches its best taste, if you are like the coffee bean, when things get worse you react better and make things around you better. How do you handle adversity? Are you a carrot, an egg or a coffee bean?